Coverall, gowns and surgical gowns part of the broader needs
Body protection provided by medical gowns and aprons or chemical (biological) protective clothing (CPC) are another form of protective equipment that is recommended to use by healthcare workers involved in the direct care of COVID-19 patients.
The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control recommends wearing at least long-sleeved water-resistant clothing to prevent body contamination. This PPE item does not need to be sterile unless it is used in a sterile environment (e.g. operating room). If MD (EN 13795-2) or PPE (EN 14126) clothing are not available, a single use plastic/water resistance apron worn over the non-water-resistant gown can be used.
The below text is obtained from document - Protective Equipment in the context of COVID-19, published by MedTech Europe on 11 May 2020 - https://www.medtecheurope.org/resource-library/protective-equipment-in-the-context-of-covid-19/’
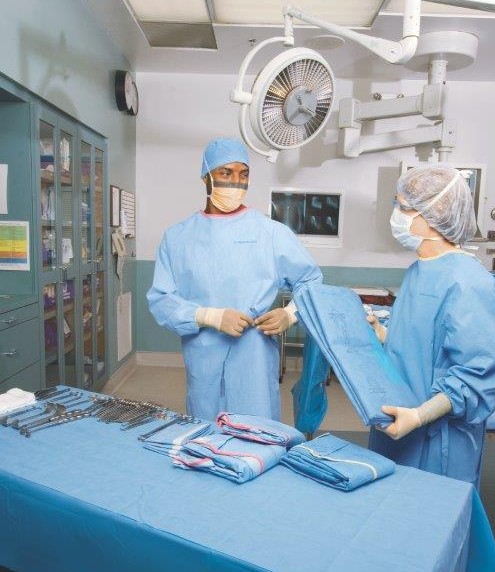
Surgical gowns
Surgical gown is a classic example of protective garment worn by surgeons during operating procedure. The general product characteristics are long sleeves with cuffs, attached waists and neck ties, adjustable neckline with yellow hook-andloop style neck binding.
If the gown is intended to provide protection to the patient, it is considered as a medical device. The relevant harmonised standards laying down the requirements for surgical garments are:
- EN 13795-1:2019 Surgical clothing and drapes - Requirements and test methods - Part 1: Surgical drapes and gowns, and
- EN 13795-2:2019 Surgical drapes, gowns and clean air suits, used as medical devices for patients, clinical staff and equipment - Part 2: Test methods
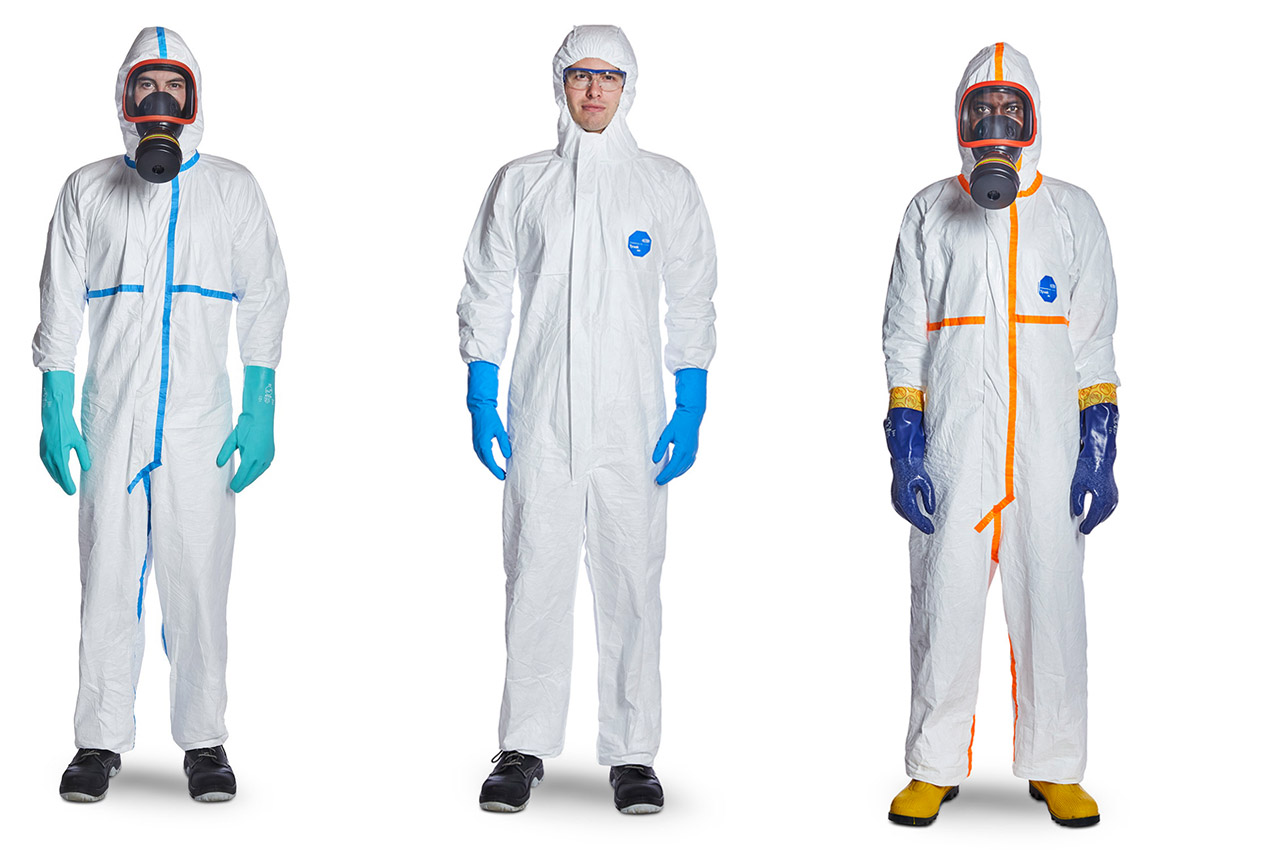

Coverall and Gowns (personal protective equipment)
Coveralls, aprons or other chemical protective clothing garments are worn for the protection of the wearer against chemicals, but also for potentially infectious material, and for the protection of the environment against potentially infectious material spread by the wearer.
Chemical (biological) protective clothing (CPC) providing body protection to the wearer are considered as PPE.
In the context of COVID-19, the relevant harmonised standard laying down the requirements for protective clothing (PPE) is EN 14126:2003 + AC 2004 Protective clothing - Performance requirements and tests methods for protective clothing against infective agents
This standard uses requirements from other chemical standards to set type tests to measure the overall imperviousness to gases, liquids (jet and spray), particulates and mists (Type 1 through Type 6)21. The most appropriate type is the Type 4 (high spray), followed by Type 6 (low spray), and by Type 5 covered respectively in EN 14605, EN 13034, EN ISO 13982 (EN 1073-2)
